selected item
3 min read
•How ExxonMobil Germany Reduced Methane Emissions by 95%
3 min read
•Around 60% of all methane emissions come from human activities – such as farming, disposing of waste, and generating energy. The remaining 40% occur naturally, mainly from wetlands.
Methane gas is the primary component of natural gas, which provides much of Europe’s energy. Natural gas fuels power stations to generate electricity and boilers to heat homes and businesses.
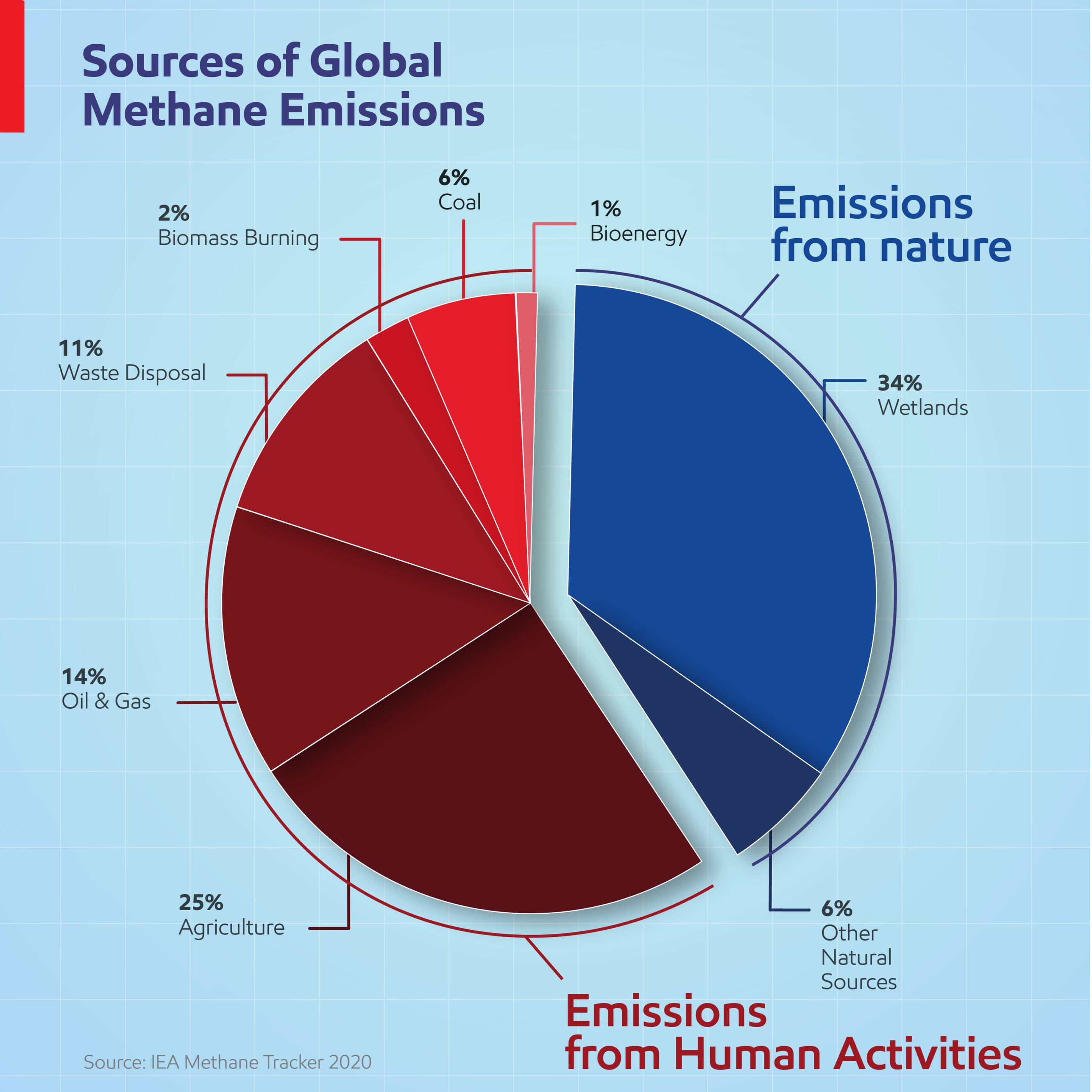
According to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Methane Tracker, the oil and gas sector accounts for around 14% of global methane emissions. Reducing and avoiding methane emissions from the energy sector where possible is therefore important, and it’s a goal supported by ExxonMobil. We are a founding signatory of the Aiming for Zero Methane Emissions Initiative announced in 2022 and are working to reach near-zero methane emissions from our operated global oil and gas assets by 2030.
ExxonMobil Germany: Achieving a 95% reduction in methane emissions
In Germany, ExxonMobil has been working to reduce methane emissions from our natural gas production since the 1990s. Through numerous initiatives, ExxonMobil Germany has reduced methane emissions from our operations by 95% in the past 20 years. Measures taken include siphoning off and burning ‘stripping gas’ during the gas drying process, and replacing ‘control gas’ with compressed air or electricity.
“The reduction of methane emissions is important from an environmental point of view,” says Pascal Weustermann, supervisor environmental engineering at ExxonMobil in Hanover. “It also makes economic sense to stop this valuable raw material from escaping. Methane that escapes during release processes or through leaks is natural gas that never gets to a customer.”
“Documenting our methane emissions has been a practice in the company since 1998,” says Ulrike Scheer, a chemical engineer and environmental and regulatory advisor at ExxonMobil in Hanover. “Since that time, we have been continually looking for and implementing ways to reduce these emissions from our operations in Germany.”
Collaborating on global action to reduce methane emissions
Close cooperation with national and supranational governments and industry associations is important and helps inform action. ExxonMobil is committed to working with the EU, the U.S. government, and others to help achieve the objectives of the Global Methane Pledge, announced in 2021.
The members of the International Association of Oil and Gas Producers (IOGP) account for almost half of the world’s oil and gas volumes. The IOGP is also one of the founding participants of the Methane Guiding Principles initiative, through which leading energy companies committed to a set of rules for reducing methane emissions in 2017.
Detecting and remedying methane leaks in natural gas infrastructure more quickly is an important aspect of reducing emissions. A global methane observatory is planned, to be built under the UN umbrella. ExxonMobil is also testing other ways to identify methane leaks. Infrared cameras, airplanes and drones, as well as satellite platforms, can all play a role. We now have extensive global know-how in reducing methane emissions and bring this to bear in regular exchanges with relevant stakeholders.
Delivering industrial solutions
Explore more

Saving Europe’s Core Industries: Cut the Red Tape
3 min read
•
The Sci-Tech Challenge: Shaping the future of STEM in Europe
5 min read
•
Europe’s industrial future is under threat – but policy reform can change that
3 min read
•
Chemical Recycling

A bone-crushing burden: Darren Woods discusses CSDDD
2 min read
•