4 min read
•Managing socioeconomic impacts
4 min read
•Navigate to:

This means maintaining high ethical standards; complying with applicable laws, rules, and regulations; and respecting local and national cultures. And we are dedicated to running safe and environmentally responsible operations.
Our Environment Policy and Protect Tomorrow. Today. guiding principle are the cornerstones of our efforts. The discipline and focus that drive our excellent reliability and safety performance drive our work to promote economic development and manage socioeconomic impacts everywhere we operate.
We base our actions on a scientific understanding of the environmental impacts of our operations. We engage with communities, governments and others early in project planning and during operations to understand the social and economic needs of the communities where we operate.
Our goal is to contribute to the social and economic progress of these communities. We believe respecting human rights, managing our impacts, and making valuable social investments are essential to our business success.
The key elements of our integrated approach include:
- Identification and assessment of potential impacts and benefits
- Human rights
- Community engagement and grievance management
- Community health, safety and security
- Local economic development
- Land use, resettlement, and livelihood restoration
- Cultural heritage
- Indigenous peoples
Impact identification and assessment
Our projects and operations around the world provide socioeconomic benefits to the communities where we operate and beyond. While there are inherent risks in any development or operation, we aim to avoid them, reduce them to acceptable levels, or remedy the impacts.
We use core processes and internal frameworks to manage our operations. Our Operations Integrity Management System (OIMS), for example, and its integrated risk management system, helps us to identify, assess, manage, and monitor environmental and socioeconomic impacts, risks and opportunities throughout the life cycles of our assets.
We use our Environmental Aspects Guide to identify and assess significant environmental and socioeconomic aspects, in line with our Environment Policy. Environmental aspects include activities, products, or services that can interact with the environment. This also covers the “human environment,” which includes social and economic aspects beyond just climate and nature.
Our processes include:
- Environmental Aspects Assessment.
- Environmental, Socioeconomic, and Health Impact Assessment.
- Environmental, Socioeconomic, and Health Management Plans.
We engage with local communities and stakeholders to understand the local socioeconomic setting, incorporate feedback, data, and other due diligence information into these processes. We periodically update our assessments and plans to reflect changes in operational complexity or socioeconomic sensitivities. When needed, we adjust our management plans accordingly.
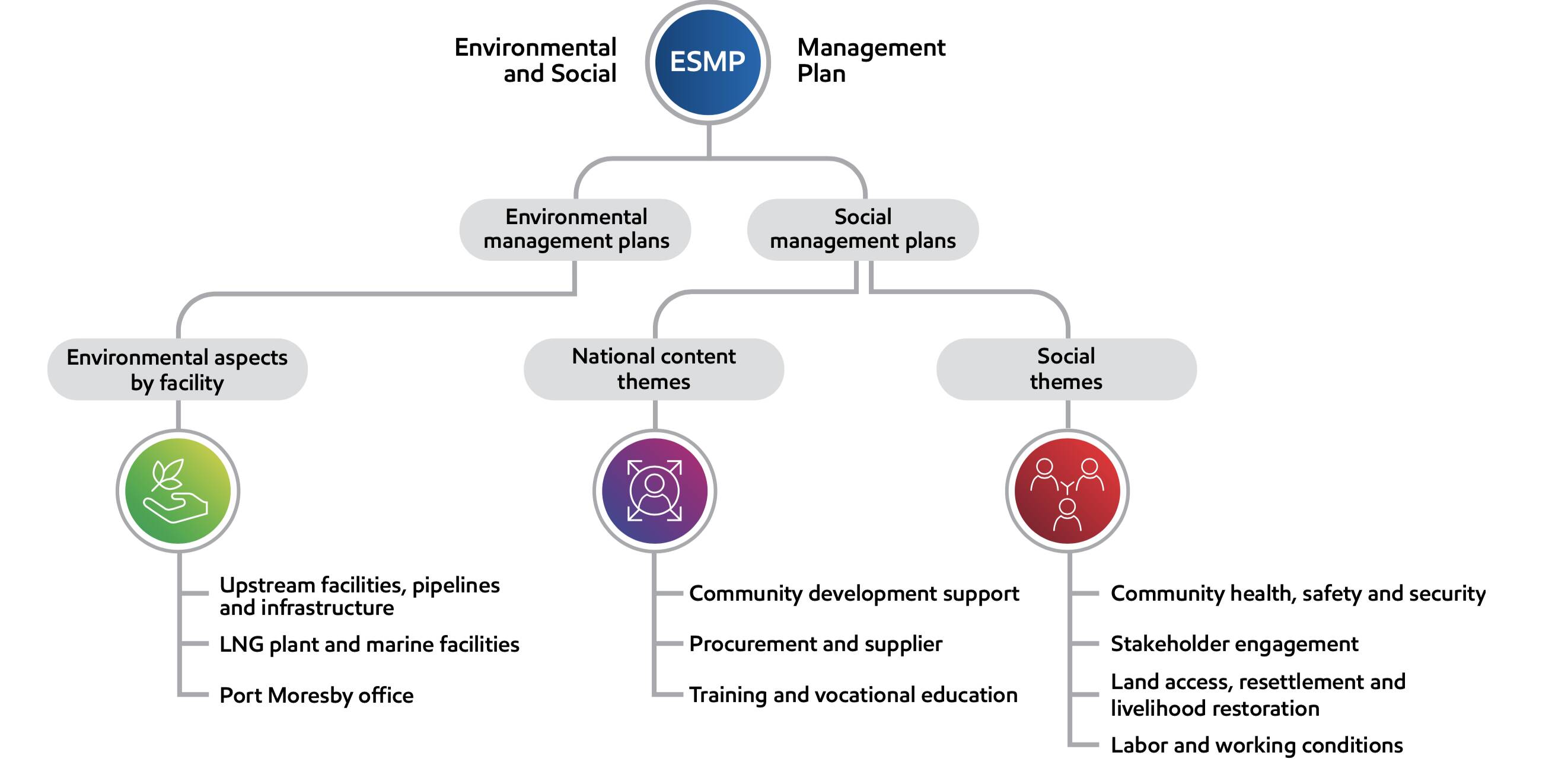
For example, at the PNG LNG project in Papua New Guinea, operated by ExxonMobil PNG Limited, the Environmental and Social Management Plan (ESMP) guides our work. It helps us manage and reduce environmental, social, community health, safety, and security impacts. The ESMP also ensures we meet Papua New Guinea’s legislative and regulatory requirements. This involves complying with more than 1,300 regulatory obligations and more than 2,700 licenses, permits, certificates, and associated conditions.
The ESMP was developed after extensive consultation with stakeholders. It includes environmental and social management and mitigation measures, monitoring requirements established by the PNG LNG Environmental Impact Statement, and lessons learned from the project’s construction phase. It also incorporates OIMS, the International Finance Corporation Performance Standards, and other international standards such as the Equator Principles.
The ESMP consists of three environmental management and seven social management plans covering all PNG LNG facilities. Requirements of the Production ESMP apply during normal operating conditions, as well as in reasonably foreseeable abnormal operating conditions or emergency situations. More information can be found in the PNG LNG 2023 Annual Report.
Community engagement and grievance management
We believe in meaningful engagement with communities to build positive, long-term relationships. We regularly consult with local groups and individuals to ensure their voices are heard and their concerns are addressed. Our engagement process is designed to be locally and culturally appropriate. We provide accessible and inclusive channels for exchanging information. This includes activities like open houses, community gatherings, and individual meetings.
By integrating results of these discussions into our decisions, we aim to avoid or reduce potential impacts on communities. This approach helps us enhance benefits, support effective investments, avoid delays, and resolve issues locally.
Grievance management
Our grievance-management process offers various platforms for individuals and communities to raise concerns. Depending on the location and nature of our activities, the process may include direct, in-person, and electronic engagement and the use of third-party proxies such as civil society organizations and nongovernmental associations. We have dedicated personnel to map, track, analyze, respond to, and resolve community grievances promptly and in a way that supports confidentiality and non-retaliation.
Our grievance-management approach involves five core steps:
- Publicize the process and support accessibility for stakeholders.
- Receive, register, and acknowledge grievances, respecting confidentiality.
- Review and investigate with the help of external input and qualified personnel.
- Develop resolution options and respond to or close out grievances.
- Monitor and evaluate outcomes.
Our practices are informed by the guidance of International Finance Corporation and Ipieca. Individual processes may be complex or simple, driven by the characteristics of each location, type of activity, local sensitivities, potential impacts, and other factors. Our key performance indicators reflect these attributes.
Managers across business lines steward programs in their areas. They are supported by community relations and subject matter experts. Management endorses and monitors these programs. This includes regular reviews of stakeholder reports, grievance summaries, and project responses.
For more information on our stakeholder engagement and grievance-management processes, see the section on Human Rights.
In practice: Environmental justice in the U.S.
We are part of the communities where our employees live and work, surrounded by their friends, families, and neighbors. Their lived experiences reinforce our belief that every community has a unique culture and history that should be respected.
We believe everyone, regardless of race, color, national origin, or income, deserves to be treated fairly. And we understand the importance of our activities to the communities where we operate and to their social and economic progress.
In places like Baytown, Beaumont, and Baton Rouge, communities have grown up around us for more than a century. Our site in Baytown opened in 1919 – nearly 30 years before the city was incorporated. Since that time, we have supported local infrastructure and housing, education and community life. 2023 highlights include:
- Supporting STEM education in the Goose Creek school district, including a $50,000 donation to their robotics division.
- Supporting higher education with a $100,000 donation to the Lee College Student Resource and Advocacy Center and equipment donations to the school’s Industrial Systems Technician Program.
- Working with local suppliers, including nearly $90 million spent with small businesses, $24.9 million with women-owned businesses, and $22.3 million with minority-owned businesses.1
In others, such as the Gulf Coast Growth Ventures (GCGV) joint-venture facility near Corpus Christi, Texas, we started operations more recently. Projects like GCGV involve hundreds of outreach meetings with local organizations, chambers, government agencies, civic groups, and neighborhoods. The GCGV Good Neighbor Program was initiated to address topics that local residents identified as most important, with four key components: Health & Safety, Education & Workforce, Environmental Stewardship, and Quality of Life. 2023 highlights include:
- >$11.5 million spent locally, including minority- and women-owned businesses and small businesses; $5 million for a new community center in Gregory, Texas.
- 8 paid interns in the inaugural class of the Process Technology Internship Program with Del Mar College.
- >$100,000 in financial support to San Patricio County Workforce Development Consortium.

Across our operations, we regularly consult with local groups and individuals so that diverse stakeholders are represented as we work alongside our communities, building on the best aspects of our operations, while mitigating any potential negative impacts.
As described in the Caring for land and biodiversity section of this report, the environmental and socioeconomic setting of our operations includes a wide range of interconnected aspects of nature, regulation, and socioeconomic sensitivities. Our policies, practices, and expectations of employees support our efforts to:
- Foster a culture of trust through inclusivity and transparency.
- Identify, mitigate, and respond effectively to the potential impacts of our operations.
- Make financial contributions and develop programs in communities to address needs or opportunities where we have some expertise or value to add.
- Work to ensure local communities directly and indirectly benefit from our presence.
As part of our engagement process, we identify and consult with potentially vulnerable and disadvantaged community members to understand barriers that may limit their participation. We tailor our processes to be accessible, inclusive, and effective in exchanging information and identifying issues.
As with everything we do, our top priority is running safe facilities for our employees and nearby residents. That’s what we’ve done for more than 140 years, and it’s what we will continue to do as we work to be an integral part of the communities in which we operate.
Community health, safety, and security
We integrate community health, safety, and security aspects into our impact assessments as a key part of our socioeconomic management approach. Our Community Health, Safety, and Security plans typically include:
- Identified risks.
- Mitigation and management measures.
- Monitoring of outcomes.
Risks assessed may include:
- Road traffic.
- Diseases spread by vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks and fleas.
- Soil, water, and sanitation-related diseases.
- Cultural health practices.
- Population shifts.
We also look for opportunities to improve health, safety, and security in the communities where we operate.
spotlight
Improving water quality in Indonesia
Since 2008, the community-based water program launched by ExxonMobil Cepu Limited in Indonesia has helped local residents access clean water during the dry season. This program aims to reduce waterborne diseases and promote healthier living.
The community established a committee to manage the budget for constructing and monitoring water facilities and distributing water. Multiple water towers have been built in the neighboring community. These towers serve as the key source of potable water, distributed to households through an installed pipeline network.
Investing in health in Guyana
Our investments in capacity in Guyana are supporting skill-based learning for students in the University of Guyana’s College of Medical Sciences. Through the Higher Education Enhancement Project, dental chairs, state-of-the-art medical equipment, anatomy models, and other items are provided to the school to prepare healthcare professionals to work in the clinical environment.
Local economic development
We work closely with local communities to understand their unique needs. Our goal is to contribute to long-term economic and social development. Our approach integrates local content and community investment into every stage of our projects.
Local content
We take a strategic, long-term approach to building human, social, and economic capacity. This approach delivers tangible, lasting benefits for people, communities, and businesses in host countries.
We focus on:
- Employing and training local personnel.
- Supporting local suppliers and contractors.
- Improving the livelihoods of community members.
We create a local content plan for each country or area. These plans set objectives for long-term economic development, considering social and economic conditions, the nature of the project, and community needs.
Local hiring and development
Hiring locally helps us meet our staffing needs and supports local economic development and education. We aim to enhance the long-term capability of the local workforce through recruitment, training, and succession planning.
We hire local individuals and help them develop technical and leadership skills. These skills benefit them throughout their careers with ExxonMobil or other future employers. Our development program includes training in:
- Relevant technical and vocational skills.
- Health and safety.
- Environmental protection.
- Management skills.
- Business conduct.
For more information view our Investing in People report.
spotlight
Economic development in Guyana
ExxonMobil Guyana Limited takes a multi-tiered approach to local content and local economic development that includes workforce development, supplier development and strategic investments. We focus on building workforce and supplier capabilities in conjunction with strategic investments in the local community.
Our strategy to develop a diverse and talented workforce has two components – the recruitment and development of Guyanese personnel who can play a role in our local operations, and the continued development of a global pool of talent capable of meeting our future business needs wherever we operate. We apply proven training curriculums, industry best practices, and leading technology to support local workforce development.
The Centre for Local Business Development, established with the help of ExxonMobil Guyana, enables local firms to learn about opportunities in the oil and gas sector, strengthen their competitiveness, and prepare to supply their various services. The Centre's entrepreneurship program called “Elevate All: The Manufacturing Edition,” has helped local professionals to build out their business framework, map their growth paths and identify opportunities for business development. Participants were offered mentorship and the opportunity to promote their products and services to banks and potential customers.
Additional information about our local content efforts in Guyana can be found at our Guyana Local Content website and in ExxonMobil Guyana’s annual report.
Local supplier development and utilization
We know the importance of building a strong, competitive supply chain in the countries where we operate. Our approach includes buying goods and services from local suppliers and helping them grow their capabilities. This helps to create a competitive local industrial base.
We collaborate with host governments, NGOs, and local communities to support local vendors. To become a supplier for ExxonMobil, a local supplier must meet our safety, technical, environmental, and human rights expectations. Our efforts support businesses owned by local individuals, women, and historically disadvantaged communities, helping them become more competitive and contributing to the long-term economic progress of the community.
Investments in local communities
Our investments support the economic development of local communities. We engage with community members, host governments, and others to develop meaningful projects. These projects aim to build and sustain economic growth while improving social conditions. We consider each community’s development goals when deciding where, when, and how to invest.
spotlight
Supporting women entrepreneurs
With funding from the ExxonMobil Foundation, the Cherie Blair Foundation for Women (CBFW) trains women in Guyana and Nigeria to build successful businesses. They work with a local partner to implement in-person and digital trainings to provide the knowledge and skills needed to start and grow their businesses.
The ExxonMobil Foundation has supported CBFW since 2015, and more than 50,000 women have been reached through their online and in-person programs.
Land use, resettlement, and livelihood restoration
We respect property rights in the countries and communities where we operate. We aim to avoid involuntary resettlement and minimize voluntary resettlement through careful site selection. When resettlement is unavoidable, our objective is to restore or improve the living standards and livelihoods of displaced people.
Site selection process
We assess multiple potential locations for our operations based on availability, accessibility, safety, and environmental and social considerations. Our screening process includes factors specific to each country, community, and area, such as:
- Local demographics.
- Employment sources and levels.
- Housing.
- Gender relations.
- Marginalized groups.
- Ecosystem services.
- Regional conflicts or tensions.
- Religious and cultural sites.
Land acquisition
If land is necessary for a project, we follow host-country regulations and our internal standards. For externally financed projects, we also adhere to lender requirements regarding land use, access, and resettlement. Resettlement is considered “involuntary” when affected individuals or communities cannot refuse, such as in cases of eminent domain. Projects requiring resettlement undergo heightened review by ExxonMobil senior management.
Resettlement and livelihood restoration
When physical or economic displacement occurs, we implement fair and transparent resettlement and compensation plans. These plans comply with regulatory requirements and recognized benchmarks like International Finance Corporation Performance Standard 5. They are tailored to the specific geographies and cultures of each location, informed by engagement with affected landowners and supported by detailed surveys of housing, gardens, wildlife, sources of nature-based products, harvesting areas, and other assets. We maintain transparency and offer a community grievance mechanism throughout the process.
spotlight
Papua New Guinea
Wherever possible, our affiliate in Papua New Guinea aims to avoid resettlement from construction activities. Where resettlement is unavoidable, the aim is to improve, or at least restore, the livelihoods and standards of living of displaced persons. Pre-construction surveys help us assess potential project impacts and determine compensation for affected families. In 2023, for example, three households were relocated from river crossings along the main pipeline route and received compensation. They were assessed for livelihood restoration support, but it was found unnecessary. A standard of living evaluation showed that two households improved their living conditions, while the third experienced a decline due to a clan dispute over compensation sharing, which is beyond the affiliate’s control.
For more information on our resettlement and livelihood restoration programs in Papua New Guinea, see the ExxonMobil PNG 2023 Environmental and Social Report.
Indigenous peoples
In locations inhabited or historically used by Indigenous peoples, we work closely with these communities to respect their cultures and customs. We support employment initiatives and cultural heritage programs through local content development and strategic community investments.
Meaningful engagement
We are committed to meaningful engagement and open consultation with Indigenous peoples. We incorporate traditional knowledge and land use practices into our plans and promote community programs that respect traditions and cultures. Meaningful engagement is a key aspect of Free, Prior, and Informed Consent, as recognized in the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
No two communities are the same. We start by establishing tailored engagement methods that align with local customs and preferences. Communities decide how they want us to engage, whether with elected leaders, community elders, or other representatives. They also choose the format – public forums, formal or informal meetings, and the frequency of these engagements.
Global frameworks
Our interactions with Indigenous peoples are consistent with the following frameworks:
- International Labour Organization Convention 169.
- United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
- International Finance Corporation Performance Standards.
- World Bank Operational Policy on Indigenous Peoples.
Imperial’s commitment to excellence in community engagement
Our majority-owned affiliate in Canada, Imperial Oil Limited, has been a leader in Canada’s energy industry for over 140 years. Imperial is crucial to our business in Canada, and it consistently demonstrates high standards, innovation, and leadership.
A key part of Imperial’s strategy to deliver value and collective success is advancing social innovation and engagement. To do this, we meaningfully support and contribute to local and Indigenous communities.

Many of Imperial’s operations are near Indigenous communities or on traditional lands. The company supports these communities where it explores, develops, and operates. The goal is to build meaningful relationships based on mutual trust, respect, and shared prosperity.
Imperial continuously works to expand relations with the Indigenous communities throughout Canada. This work is supported by its Indigenous relations and principles guidelines, which are built on four key pillars of engagement.
Imperial is a Canadian Council for Aboriginal Business procurement champion. This places it among a select group of corporations committed to increasing supply chain opportunities for Indigenous Businesses.
Indigenous stakeholders have told Imperial that one of the most meaningful contributions it can make is to build strong partnerships with Indigenous businesses. Imperial has worked to connect Indigenous and non-Indigenous suppliers and align its national supply chain needs with Indigenous partner capacity
In 2021, Imperial reached a significant milestone, signing its largest-ever contracts with Indigenous-owned companies, Fort McKay Graham and Mikisew North American. They were awarded five-year contracts for large-scale earthwork, land reclamation, and mining support services. This led to record spending with Indigenous suppliers.
Imperial is now focused on expanding these efforts across the value chain, especially in downstream operations. It continues to incorporate Indigenous input and traditional knowledge into its projects. Imperial is also increasing Indigenous representation in its workforce and enhancing cultural education for its employees across Canada.
Cultural Heritage
Our respect for the cultural heritage and customs of local communities carries into our business practices. We do this by managing the potential impacts of our operations and by making culturally appropriate community investments.
From project design to our ongoing operations, we look for ways to help preserve cultural heritage. As we design our projects, we consider cultural and spiritual considerations, heritage sites, biodiversity conservation, traditional knowledge, and efficient use of resources.
We value and respect the diverse cultural histories of the areas where we operate. To do this, we identify potential sites of cultural significance. If the recovery or relocation of an artifact is appropriate, we develop tailored procedures in consultation with technical experts, local communities, and host country government officials.
We also deepen our knowledge with relevant research. And we provide training to our construction and field contractor personnel. This helps them identify different types of cultural heritage in the areas where we work.
Publications
Explore more

Expanding the plastics life cycle
3 min read
•
Integrating sustainability into what we do
5 min read
•
Working with suppliers

Enhancing process safety
3 min read
•
Improving air quality
2 min read
•FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENT WARNING
Images or statements of future ambitions, aims, aspirations, plans, goals, events, projects, projections, opportunities, expectations, performance, or conditions in the publications, including plans to reduce, abate, avoid or enable avoidance of emissions or reduce emissions intensity, sensitivity analyses, expectations, estimates, the development of future technologies, business plans, and sustainability efforts are dependent on future market factors, such as customer demand, continued technological progress, stable policy support and timely rule-making or continuation of government incentives and funding, and represent forward-looking statements. Similarly, emission-reduction roadmaps to drive toward net zero and similar roadmaps for emerging technologies and markets, and water management roadmaps to reduce freshwater intake and/or manage disposal, are forward-looking statements. These statements are not guarantees of future corporate, market or industry performance or outcomes for ExxonMobil or society and are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control or are even unknown.
Actual future results, including the achievement of ambitions to reach Scope 1 and 2 net zero from operated assets by 2050, to reach Scope 1 and 2 net zero in heritage Permian Basin unconventional operated assets by 2030, and in Pioneer Permian assets by 2035, to eliminate routine flaring in-line with World Bank Zero Routine Flaring, to reach near zero methane emissions from operated assets and other methane initiatives to meet ExxonMobil’s greenhouse gas emission reduction plans and goals, divestment and start-up plans, and associated project plans as well as technology advances, including in the timing and outcome of projects to capture, transport and store CO2, produce hydrogen and ammonia, produce lower-emission fuels, produce ProxximaTM systems, produce carbon materials, produce lithium, and use plastic waste as feedstock for advanced recycling; future debt levels and credit ratings; business and project plans, timing, costs, capacities and profitability; resource recoveries and production rates; planned Denbury and Pioneer integrated benefits; obtain data on detection, measurement and quantification of emissions including reporting of that data or updates to previous estimates and progress in sustainability focus areas could vary depending on a number of factors, including global or regional changes in oil, gas, petrochemicals, or feedstock prices, differentials, seasonal fluctuations, or other market or economic conditions affecting the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries and the demand for our products; new market products and services; future cash flows; our ability to execute operational objectives on a timely and successful basis; the ability to realize efficiencies within and across our business lines; new or changing government policies for lower carbon and new market investment opportunities, or policies limiting the attractiveness of investments such as European taxes on energy and unequal support for different methods of carbon capture; developments or changes in local, national, or international treaties, laws, regulations, taxes, trade sanctions, trade tariffs, and incentives affecting our business, including those related to greenhouse gas emissions, plastics, carbon storage and carbon costs; timely granting of governmental permits and certifications; uncertain impacts of deregulation on the legal and regulatory environment; evolving reporting standards for these topics and evolving measurement standards for reported data; trade patterns and the development and enforcement of local, national and regional mandates; unforeseen technical or operational difficulties; the outcome of research efforts and future technology developments, including the ability to scale projects and technologies such as electrification of operations, advanced recycling, carbon capture and storage, hydrogen and ammonia production, ProxximaTM systems, carbon materials or direct lithium extraction on a commercially competitive basis; the development and competitiveness of alternative energy and emission reduction technologies; unforeseen technical or operating difficulties, including the need for unplanned maintenance; availability of feedstocks for lower-emission fuels, hydrogen, or advanced recycling; changes in the relative energy mix across activities and geographies; the actions of co-venturers competitors; changes in regional and global economic growth rates and consumer preferences including willingness and ability to pay for reduced emissions products; actions taken by governments and consumers resulting from a pandemic; changes in population growth, economic development or migration patterns; timely completion of construction projects; war, civil unrest, attacks against the Company or industry, and other political or security disturbances, including disruption of land or sea transportation routes; decoupling of economies, realignment of global trade and supply chain networks, and disruptions in military alliances; and other factors discussed here and in Item 1A. Risk Factors of our Annual Report on Form 10-K and under the heading “Factors affecting future results” available under the “Earnings” tab through the “Investors” page of our website at www.exxonmobil.com. The Advancing Climate Solutions Report includes 2024 greenhouse gas emissions performance data as of March 1, 2025, and Scope 3 Category 11 estimates for full year 2024 as of February 19, 2025. The greenhouse gas intensity and greenhouse gas emission estimates include Scope 2 market-based emissions. The Sustainability Report, the Advancing Climate Solutions Report, and corresponding Executive Summaries were issued on April 30, 2025. The content and data referenced in these publications focus primarily on our operations from Jan. 1, 2024 – Dec. 31, 2024, unless otherwise indicated. Tables on our “Metrics and data” page were updated to reflect full year 2024 data. Information regarding some known events or activities in 2025 and historical initiatives from prior years are also included. No party should place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the dates of these publications. All forward-looking statements are based on management’s knowledge and reasonable expectations at the time of publication. ExxonMobil assumes no duty to update these statements or materials as of any future date, and neither future distribution of this material nor the continued availability of this material in archive form on our website should be deemed to constitute an update or re-affirmation of these figures or statements as of any future date. Any future update will be provided only through a public disclosure indicating that fact.
See “ABOUT THE ADVANCING CLIMATE SOLUTIONS AND SUSTAINABILITY REPORTS” at the end of this document for additional information on these reports and the use of non-GAAP and other financial measures.
ABOUT THE ADVANCING CLIMATE SOLUTIONS AND SUSTAINABILITY REPORTS
The Advancing Climate Solutions Report contains terms used by the TCFD, as well as information about how the disclosures in this report are consistent with the recommendations of the TCFD. In doing so, ExxonMobil is not obligating itself to use any terms in the way defined by the TCFD or any other party, nor is it obligating itself to comply with any specific recommendation of the TCFD or to provide any specific disclosure. For example, with respect to the term “material,” individual companies are best suited to determine what information is material, under the long-standing U.S. Supreme Court definition, and whether to include this information in U.S. Securities and Exchange Act filings. In addition, the ISSB is evaluating standards that provide their interpretation of TCFD which may or may not be consistent with the current TCFD recommendations. The Sustainability Report and Advancing Climate Solutions Report are each a voluntary disclosure and are not designed to fulfill any U.S., foreign, or third-party required reporting framework.
Forward-looking and other statements regarding environmental and other sustainability efforts and aspirations are not intended to communicate any material investment information under the laws of the United States or represent that these are required disclosures. These publications are not intended to imply that ExxonMobil has access to any significant non-public insights on future events that the reader could not independently research. In addition, historical, current, and forward-looking environmental and other sustainability-related statements may be based on standards for measuring progress that are still developing, internal controls and processes that continue to evolve, and assumptions that are subject to change in the future, including future laws and rulemaking. Forward-looking and other statements regarding environmental and other sustainability efforts and aspirations are for informational purposes only and are not intended as an advertisement for ExxonMobil’s equity, debt, businesses, products, or services and the reader is specifically notified that any investor-requested disclosure or future required disclosure is not and should not be construed as an inducement for the reader to purchase any product or services. The statements and analysis in these publications represent a good faith effort by the Company to address these investor requests despite significant unknown variables and, at times, inconsistent market data, government policy signals, and calculation, methodologies, or reporting standards.
Actions needed to advance ExxonMobil’s 2030 greenhouse gas emission-reductions plans are incorporated into its medium-term business plans, which are updated annually. The reference case for planning beyond 2030 is based on the Company’s Global Outlook research and publication. The Global Outlook is reflective of the existing global policy environment and an assumption of increasing policy stringency and technology improvement to 2050. However, the Global Outlook does not attempt to project the degree of required future policy and technology advancement and deployment for the world, or ExxonMobil, to meet net zero by 2050. As future policies and technology advancements emerge, they will be incorporated into the GIobal Outlook, and the Company’s business plans will be updated as appropriate. References to projects or opportunities may not reflect investment decisions made by the corporation or its affiliates. Individual projects or opportunities may advance based on a number of factors, including availability of stable and supportive policy, permitting, technological advancement for cost-effective abatement, insights from the Company planning process, and alignment with our partners and other stakeholders. Capital investment guidance in lower-emission and other new investments is based on our corporate plan; however, actual investment levels will be subject to the availability of the opportunity set, stable public policy support, other factors, and focused on returns.
Energy demand modeling aims to replicate system dynamics of the global energy system, requiring simplifications. The reference to any scenario or any pathway for an energy transition, including any potential net-zero scenario, does not imply ExxonMobil views any particular scenario as likely to occur. In addition, energy demand scenarios require assumptions on a variety of parameters. As such, the outcome of any given scenario using an energy demand model comes with a high degree of uncertainty. For example, the IEA describes its NZE scenario as extremely challenging, requiring unprecedented innovation, unprecedented international cooperation, and sustained support and participation from consumers, with steeper reductions required each year since the scenario’s initial release. Third-party scenarios discussed in these reports reflect the modeling assumptions and outputs of their respective authors, not ExxonMobil, and their use or inclusion herein is not an endorsement by ExxonMobil of their underlying assumptions, likelihood, or probability. Investment decisions are made on the basis of ExxonMobil’s separate planning process but may be secondarily tested for robustness or resiliency against different assumptions, including against various scenarios. These reports contain information from third parties. ExxonMobil makes no representation or warranty as to the third-party information. Where necessary, ExxonMobil received permission to cite third-party sources, but the information and data remain under the control and direction of the third parties. ExxonMobil has also provided links in this report to third-party websites for ease of reference. ExxonMobil’s use of the third-party content is not an endorsement or adoption of such information.
ExxonMobil reported emissions, including reductions and avoidance performance data, are based on a combination of measured and estimated data. We assess our performance to support continuous improvement throughout the organization using our Environmental Performance Indicator (EPI) manual. The reporting guidelines and indicators in the Ipieca, the American Petroleum Institute (API), the International Association of Oil and Gas Producers Sustainability Reporting Guidance for the Oil and Gas Industry (4th edition, 2020, revised February 2023) and key chapters of the GHG Protocol inform the EPI and the selection of the data reported. Emissions reported are estimates only, and performance data depends on variations in processes and operations, the availability of sufficient data, the quality of those data and methodology used for measurement and estimation. Emissions data is subject to change as methods, data quality, and technology improvements occur, and changes to performance data may be updated. Emissions, reductions, abatements and enabled avoidance estimates for non-ExxonMobil operated facilities are included in the equity data and similarly may be updated as changes in the performance data are reported. ExxonMobil’s plans to reduce emissions are good-faith efforts based on current relevant data and methodology, which could be changed or refined. ExxonMobil works to continuously improve its approach to estimate, detect, measure, and address emissions. ExxonMobil actively engages with industry, including API and Ipieca, to improve emission factors and methodologies, including measurements and estimates.
Any reference to ExxonMobil’s support of, work with, or collaboration with a third-party organization within these publications do not constitute or imply an endorsement by ExxonMobil of any or all of the positions or activities of such organization. ExxonMobil participates, along with other companies, institutes, universities and other organizations, in various initiatives, campaigns, projects, groups, trade organizations, and other collaborations among industry and through organizations like the United Nations that express various ambitions, aspirations and goals related to climate change, emissions, sustainability, and the energy transition. ExxonMobil’s participation or membership in such collaborations is not a promise or guarantee that ExxonMobil’s individual ambitions, future performance or policies will align with the collective ambitions of the organizations or the individual ambitions of other participants, all of which are subject to a variety of uncertainties and other factors, many of which may be beyond ExxonMobil’s control, including government regulation, availability and cost-effectiveness of technologies, and market forces and other risks and uncertainties. Such third parties’ statements of collaborative or individual ambitions and goals frequently diverge from ExxonMobil’s own ambitions, plans, goals, and commitments. ExxonMobil will continue to make independent decisions regarding the operation of its business, including its climate-related and sustainability-related ambitions, plans, goals, commitments, and investments. ExxonMobil’s future ambitions, goals and commitments reflect ExxonMobil’s current plans, and ExxonMobil may unilaterally change them for various reasons, including adoption of new reporting standards or practices, market conditions; changes in its portfolio; and financial, operational, regulatory, reputational, legal and other factors.
References to “resources,” “resource base,” “recoverable resources” and similar terms refer to the total remaining estimated quantities of oil and natural gas that are expected to be ultimately recoverable. The resource base includes quantities of oil and natural gas classified as proved reserves, as well as quantities that are not yet classified as proved reserves, but that are expected to be ultimately recoverable. The term “resource base” is not intended to correspond to SEC definitions such as “probable” or “possible” reserves. For additional information, see the “Frequently Used Terms” on the Investors page of the Company’s website at www.exxonmobil.com under the header “Modeling Toolkit.” References to “oil” and “gas” include crude, natural gas liquids, bitumen, synthetic oil, and natural gas. The term “project” as used in these publications can refer to a variety of different activities and does not necessarily have the same meaning as in any government payment transparency reports.
Exxon Mobil Corporation has numerous affiliates, many with names that include ExxonMobil, Exxon, Mobil, Esso, and XTO. For convenience and simplicity, those terms and terms such as “Corporation,” “company,” “our,” “we,” and “its” are sometimes used as abbreviated references to one or more specific affiliates or affiliate groups. Abbreviated references describing global or regional operational organizations, and global or regional business lines are also sometimes used for convenience and simplicity. Nothing contained herein is intended to override the corporate separateness of affiliated companies. Exxon Mobil Corporation’s goals do not guarantee any action or future performance by its affiliates or Exxon Mobil Corporation’s responsibility for those affiliates’ actions and future performance, each affiliate of which manages its own affairs. For convenience and simplicity, words like venture, joint venture, partnership, co-venturer and partner are used to indicate business relationships involving common activities and interests, and those words may not indicate precise legal relationships. These publications cover Exxon Mobil Corporation’s owned and operated businesses and do not address the performance or operations of our suppliers, contractors or partners unless otherwise noted. In the case of certain joint ventures for which ExxonMobil is the operator, we often exercise influence but not control. Thus, the governance, processes, management and strategy of these joint ventures may differ from those in these reports. At the time of publication, ExxonMobil has completed the acquisitions of Denbury Inc. and Pioneer Natural Resources Company. These reports and the data therein do not speak of these companies’ pre-acquisition governance, risk management, strategy approaches, or emissions or sustainability performance unless specifically referenced.
These reports or any material therein are not to be used or reproduced without the permission of Exxon Mobil Corporation. All rights reserved.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR NON-GAAP AND OTHER MEASURES
The Positioned for Growth in a Lower-Emission Future section of the Advancing Climate Solutions Report mentions modeled operating cash flow in comparing different businesses over time in a future scenario. Historic operating cash flow is defined as net income, plus depreciation, depletion and amortization for consolidated and equity companies, plus noncash adjustments related to asset retirement obligations plus proceeds from asset sales. The Company’s long-term portfolio modeling estimates operating cash flow as revenue or margins less cash expenses, taxes and abandonment expenditures plus proceeds from asset sales before portfolio capital expenditures. The Company believes this measure can be helpful in assessing the resiliency of the business to generate cash from different potential future markets. The performance data presented in the Advancing Climate Solutions Report and Sustainability Report, including on emissions, is not financial data and is not GAAP data.




