3 min read
•Expanding the plastics life cycle
3 min read
•Navigate to:
Plastic products help defend against disease, preserve food, and are used in medical equipment that saves lives.
As described in our Global Outlook, prosperity and population are expected to grow around the world between now and 2050. Plastics will be instrumental in supporting many of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, including good health, food preservation, and clean drinking water.
As living standards increase, plastics allow society to do more with less material and often with a smaller environmental footprint than alternatives. A recent U.S.-based study found that polyethylene (PE) packaging—the most widely used plastic packaging—can reduce lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to alternative materials like glass, paper, and aluminum.1
In transportation, plastics enable lighter vehicles, driving a 6% to 8% fuel efficiency gain for every 10% reduction in weight.2 The electric vehicle industry also relies on plastics to produce lightweight cars to extend battery range.
In agriculture, the plastic films made from our polymers support farming around the world by enabling:
- Durable solutions for greenhouses that help farmers grow their crops all year long.
- Long-lasting mulch solutions that use less material and help increase crop production rates by reducing the frequent need to collect and replace used plastic film.
- Tough, puncture-resistant films for grain silos to reduce loss and spoilage.
Plastics are increasingly society’s material of choice due to their functional benefits and have overall lower life cycle greenhouse gas emissions compared to alternative materials in most applications.
Our approach
To meet society’s evolving needs, our efforts are focused both on enabling the societal benefits plastics provide and helping address the global issue of plastic waste. Our approach includes:
- Expanding our advanced recycling capacity to help further broaden the range of plastics that can be recycled;
- Developing plastic solutions that enable our customers to make products that use less plastic; and
- Supporting improvements in plastic waste recovery, gathering, and sorting.
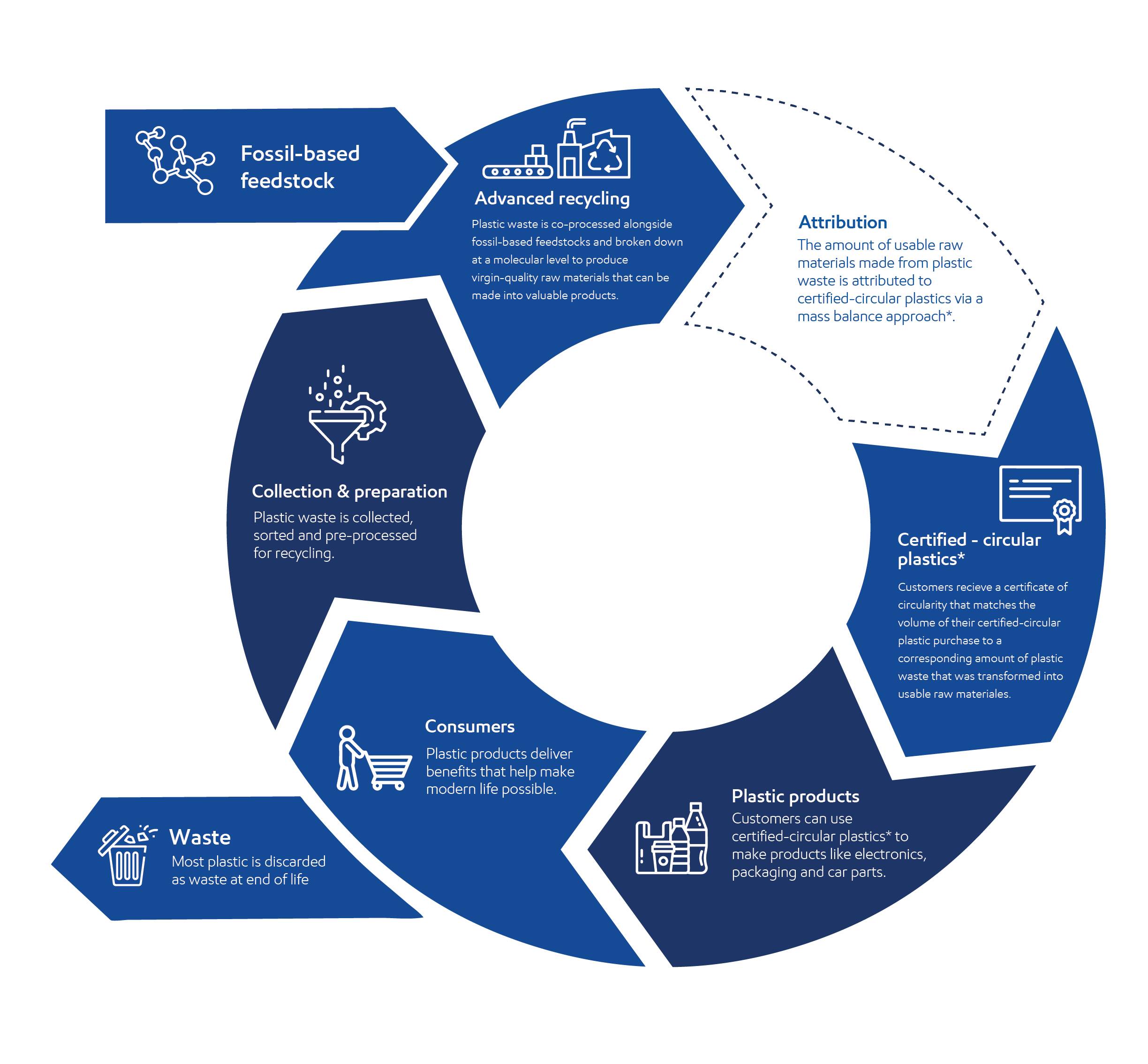
Supporting a more circular economy for plastics with advanced recycling
Mismanaged plastic waste is a global problem. We believe that a more circular economy for plastics is an important part of the solution.
Around the world, only about 9% of all plastics are recycled.3 Even in areas with better waste and recycling infrastructure, like the European Union, less than 27% of plastic waste is recycled4 once it leaves consumers’ hands. The rest is burned for energy, goes to landfills, or is discarded to the environment.
There are better uses for these materials.
We are helping to address the plastic waste challenge through advanced recycling (sometimes called chemical recycling) – giving plastic waste another life as new products that people need.
Many products are difficult to recycle through mechanical recycling – the traditional method of grinding and melting plastic waste. But when both are used, mechanical recycling and advanced recycling could enable more types of plastic waste to be recycled.
With advanced recycling, plastic waste is broken down at the molecular level. This allows even complex blends of plastics to be turned back into usable raw materials. These are identical to the raw materials produced during the processing of fossil-based feedstocks and can be used to make a wide range of valuable products, including fuels, lubricants, and high-performance chemicals and plastics.
ExxonMobil’s technology for advanced recycling is not burning waste, which would consume the molecules and make it impossible to make new products out of them. Instead, we use a technology called “pyrolysis” to convert about 90% of the processed plastic waste into usable raw materials – a highly efficient process. For every ton of certified-circular plastics sold, more than a ton of plastic waste avoids other end-of-life dispositions like landfill or incineration.5
~ 1 ton
Does not represent GHG emissions or recycled content.
We sell certified-circular plastics corresponding to the amount of plastic waste we transform back into usable raw materials. We do this using a mass balance approach that has been used in other industries for many years.
What is mass balance? In short, it is an accounting process that can be used in complex value chains like ours in which one input (e.g., plastic waste) is mixed with other inputs in a way that the different inputs cannot be physically traced throughout the system. This widely used approach helps our customers match the volume of their certified-circular plastic purchase to a corresponding amount of plastic waste that we transformed into usable raw materials through advanced recycling.
Similar concepts are used in other sectors to help customers and society keep track of their impact. For example, if you buy “renewable energy” from your electricity provider, you’re paying for that energy to be generated and added to the grid, but the electricity that reaches your house might come from a mix of sources.
Our advanced recycling facilities and process are certified via an independent, third-party certification system called International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC) PLUS. ISCC is an association of more than 240 members, including research institutes and NGOs.
The certificate we provide our customers is not a claim that our certified-circular plastics contain specific amounts of “recycled content” or carry GHG benefits. Rather, it represents an assurance that we followed a rigorous mass balance attribution system that is certified by a third-party. This enables us to be transparent about our products, helping our customers, and their customers, progress and communicate circularity goals.
Scaling up capacity to meet growing demand
There is rising demand from consumers and customers for circularity, far more than mechanical recycling can provide. Purchasing certified-circular plastics can enable our customers to achieve circularity goals, such as:
- Unlocking the value of plastic waste by converting it into useful raw materials;
- Monetizing the value of plastic waste to drive better collection and sorting;
- Contributing to the growth of the recycling sector; and
- Accelerating plastic recycling rates.

We are uniquely positioned with our scale, integration, and technology to rapidly expand advanced recycling capacity and help meet the needs of our customers and communities. Customers so far include Sealed Air, Ahold Delhaize, Berry Global, Pactiv Evergreen, and Amcor, all supporting a more circular economy for food packaging.
Our Baytown advanced recycling facility started up commercial-scale operations in December 2022. In late 2024, we announced plans to invest more than $200 million to expand advanced recycling operations in Baytown and Beaumont, Texas. The investment will add 350 million pounds per year of advanced recycling capacity at these two sites, bringing our total capacity to 500 million pounds per year.
As of December 2024, our Baytown site has processed more than 80 million pounds of end-of-life plastic – with more to come as we collaborate to get more plastic collected, sorted, and ready to process.
We are continuing to develop additional advanced recycling projects at manufacturing sites in North America, Europe and Asia, with the goal of reaching 1 billion pounds per year of advanced recycling capacity globally.
Increasing recycling rates through collaboration and innovation
Like most complex environmental challenges, broad collaboration is needed to address the issue of mismanaged waste. This includes sound policy and investment in waste-management infrastructure. Through organizations such as the Alliance to End Plastic Waste, we collaborate across the value chain to increase plastic waste collection and sorting to help support a more circular economy for plastics.
In December 2023, Cyclyx, our joint venture with Agilyx Corp. and LyondellBasell, announced plans to build its first Cyclyx Circularity Center (CCC). This first-of-its-kind plastic waste processing facility will have the capacity to produce 300 million pounds of plastic feedstock per year to be used in both advanced and mechanical recycling of post-consumer, commercial, and industrial plastic waste. As a founding member of the Houston Recycling Collaboration, ExxonMobil is working with others in industry and government to increase access to plastic recycling in the Houston area in support of the CCC.
Responsible manufacturing: the right products the right way
Our VistmaxxTM performance polymers make recycling easier by making polyethylene and polypropylene more compatible, which allows them to “mix in the melt” and removes the need for mechanical recyclers to separate these materials for processing.
Collaboration, again, leads to even better results. For example, ExxonMobil Asia Pacific Research & Development Co., Ltd partnered with Shantou Mingca Packaging earlier this year on an ultra-low density shrink film that can be manufactured with minimal adjustments in production lines. More importantly, it can be more easily recycled in communities with programs and facilities in place to collect plastic film, even by traditional recyclers, as certified by TÜV Rheinland, a global leader in inspection services.
Our efforts are further supported by our systems to responsibly manage plastics manufacturing, including the global standards we have set across all of our resin-handling operations. These standards are more stringent than the laws and regulations related to plastic pellet loss in many of the places we operate, and we collaborate with industry through Operation Clean Sweep-Blue to share best practices.7
-
Meeting society's critical needs for energy and products
Publications
Explore more

Integrating sustainability into what we do
5 min read
•
Working with suppliers

Enhancing process safety
3 min read
•
Improving air quality
2 min read
•
Sustainability Report Executive Summary
5 min read
•FOOTNOTES:
- Based on the 2025 study “Polyethylene packaging and alternative materials in the United States: A life cycle assessment” (Science of the Total Environment). Full study: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969724085176?via%3Dihub.
- Department of Energy statements at https://www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles/lightweight-materials-cars-and-trucks.
- Based on OECD Global Plastics Outlook: https://www.oecd.org/content/dam/oecd/en/publications/reports/2022/02/global-plastics-outlook_a653d1c9/de747aef-en.pdf
- Plastics Europe: The Circular Economy for Plastics: A European Analysis
- Certified-circular plastics are virgin-quality plastics that are accompanied by a certificate that matches the mass of virgin quality plastics that we sell to a corresponding amount of plastic waste that we transformed back into usable raw materials through advanced recycling.
- On a global, macroeconomic basis, assuming constant demand.
- Pellet loss refers to the unintended release of plastic resin into the environment during manufacturing, transportation, handling, or processing.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENT WARNING
Images or statements of future ambitions, aims, aspirations, plans, goals, events, projects, projections, opportunities, expectations, performance, or conditions in the publications, including plans to reduce, abate, avoid or enable avoidance of emissions or reduce emissions intensity, sensitivity analyses, expectations, estimates, the development of future technologies, business plans, and sustainability efforts are dependent on future market factors, such as customer demand, continued technological progress, stable policy support and timely rule-making or continuation of government incentives and funding, and represent forward-looking statements. Similarly, emission-reduction roadmaps to drive toward net zero and similar roadmaps for emerging technologies and markets, and water management roadmaps to reduce freshwater intake and/or manage disposal, are forward-looking statements. These statements are not guarantees of future corporate, market or industry performance or outcomes for ExxonMobil or society and are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control or are even unknown.
Actual future results, including the achievement of ambitions to reach Scope 1 and 2 net zero from operated assets by 2050, to reach Scope 1 and 2 net zero in heritage Permian Basin unconventional operated assets by 2030, and in Pioneer Permian assets by 2035, to eliminate routine flaring in-line with World Bank Zero Routine Flaring, to reach near zero methane emissions from operated assets and other methane initiatives to meet ExxonMobil’s greenhouse gas emission reduction plans and goals, divestment and start-up plans, and associated project plans as well as technology advances, including in the timing and outcome of projects to capture, transport and store CO2, produce hydrogen and ammonia, produce lower-emission fuels, produce ProxximaTM systems, produce carbon materials, produce lithium, and use plastic waste as feedstock for advanced recycling; future debt levels and credit ratings; business and project plans, timing, costs, capacities and profitability; resource recoveries and production rates; planned Denbury and Pioneer integrated benefits; obtain data on detection, measurement and quantification of emissions including reporting of that data or updates to previous estimates and progress in sustainability focus areas could vary depending on a number of factors, including global or regional changes in oil, gas, petrochemicals, or feedstock prices, differentials, seasonal fluctuations, or other market or economic conditions affecting the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries and the demand for our products; new market products and services; future cash flows; our ability to execute operational objectives on a timely and successful basis; the ability to realize efficiencies within and across our business lines; new or changing government policies for lower carbon and new market investment opportunities, or policies limiting the attractiveness of investments such as European taxes on energy and unequal support for different methods of carbon capture; developments or changes in local, national, or international treaties, laws, regulations, taxes, trade sanctions, trade tariffs, and incentives affecting our business, including those related to greenhouse gas emissions, plastics, carbon storage and carbon costs; timely granting of governmental permits and certifications; uncertain impacts of deregulation on the legal and regulatory environment; evolving reporting standards for these topics and evolving measurement standards for reported data; trade patterns and the development and enforcement of local, national and regional mandates; unforeseen technical or operational difficulties; the outcome of research efforts and future technology developments, including the ability to scale projects and technologies such as electrification of operations, advanced recycling, carbon capture and storage, hydrogen and ammonia production, ProxximaTM systems, carbon materials or direct lithium extraction on a commercially competitive basis; the development and competitiveness of alternative energy and emission reduction technologies; unforeseen technical or operating difficulties, including the need for unplanned maintenance; availability of feedstocks for lower-emission fuels, hydrogen, or advanced recycling; changes in the relative energy mix across activities and geographies; the actions of co-venturers competitors; changes in regional and global economic growth rates and consumer preferences including willingness and ability to pay for reduced emissions products; actions taken by governments and consumers resulting from a pandemic; changes in population growth, economic development or migration patterns; timely completion of construction projects; war, civil unrest, attacks against the Company or industry, and other political or security disturbances, including disruption of land or sea transportation routes; decoupling of economies, realignment of global trade and supply chain networks, and disruptions in military alliances; and other factors discussed here and in Item 1A. Risk Factors of our Annual Report on Form 10-K and under the heading “Factors affecting future results” available under the “Earnings” tab through the “Investors” page of our website at www.exxonmobil.com. The Advancing Climate Solutions Report includes 2024 greenhouse gas emissions performance data as of March 1, 2025, and Scope 3 Category 11 estimates for full year 2024 as of February 19, 2025. The greenhouse gas intensity and greenhouse gas emission estimates include Scope 2 market-based emissions. The Sustainability Report, the Advancing Climate Solutions Report, and corresponding Executive Summaries were issued on April 30, 2025. The content and data referenced in these publications focus primarily on our operations from Jan. 1, 2024 – Dec. 31, 2024, unless otherwise indicated. Tables on our “Metrics and data” page were updated to reflect full year 2024 data. Information regarding some known events or activities in 2025 and historical initiatives from prior years are also included. No party should place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the dates of these publications. All forward-looking statements are based on management’s knowledge and reasonable expectations at the time of publication. ExxonMobil assumes no duty to update these statements or materials as of any future date, and neither future distribution of this material nor the continued availability of this material in archive form on our website should be deemed to constitute an update or re-affirmation of these figures or statements as of any future date. Any future update will be provided only through a public disclosure indicating that fact.
See “ABOUT THE ADVANCING CLIMATE SOLUTIONS AND SUSTAINABILITY REPORTS” at the end of this document for additional information on these reports and the use of non-GAAP and other financial measures.
ABOUT THE ADVANCING CLIMATE SOLUTIONS AND SUSTAINABILITY REPORTS
The Advancing Climate Solutions Report contains terms used by the TCFD, as well as information about how the disclosures in this report are consistent with the recommendations of the TCFD. In doing so, ExxonMobil is not obligating itself to use any terms in the way defined by the TCFD or any other party, nor is it obligating itself to comply with any specific recommendation of the TCFD or to provide any specific disclosure. For example, with respect to the term “material,” individual companies are best suited to determine what information is material, under the long-standing U.S. Supreme Court definition, and whether to include this information in U.S. Securities and Exchange Act filings. In addition, the ISSB is evaluating standards that provide their interpretation of TCFD which may or may not be consistent with the current TCFD recommendations. The Sustainability Report and Advancing Climate Solutions Report are each a voluntary disclosure and are not designed to fulfill any U.S., foreign, or third-party required reporting framework.
Forward-looking and other statements regarding environmental and other sustainability efforts and aspirations are not intended to communicate any material investment information under the laws of the United States or represent that these are required disclosures. These publications are not intended to imply that ExxonMobil has access to any significant non-public insights on future events that the reader could not independently research. In addition, historical, current, and forward-looking environmental and other sustainability-related statements may be based on standards for measuring progress that are still developing, internal controls and processes that continue to evolve, and assumptions that are subject to change in the future, including future laws and rulemaking. Forward-looking and other statements regarding environmental and other sustainability efforts and aspirations are for informational purposes only and are not intended as an advertisement for ExxonMobil’s equity, debt, businesses, products, or services and the reader is specifically notified that any investor-requested disclosure or future required disclosure is not and should not be construed as an inducement for the reader to purchase any product or services. The statements and analysis in these publications represent a good faith effort by the Company to address these investor requests despite significant unknown variables and, at times, inconsistent market data, government policy signals, and calculation, methodologies, or reporting standards.
Actions needed to advance ExxonMobil’s 2030 greenhouse gas emission-reductions plans are incorporated into its medium-term business plans, which are updated annually. The reference case for planning beyond 2030 is based on the Company’s Global Outlook research and publication. The Global Outlook is reflective of the existing global policy environment and an assumption of increasing policy stringency and technology improvement to 2050. However, the Global Outlook does not attempt to project the degree of required future policy and technology advancement and deployment for the world, or ExxonMobil, to meet net zero by 2050. As future policies and technology advancements emerge, they will be incorporated into the GIobal Outlook, and the Company’s business plans will be updated as appropriate. References to projects or opportunities may not reflect investment decisions made by the corporation or its affiliates. Individual projects or opportunities may advance based on a number of factors, including availability of stable and supportive policy, permitting, technological advancement for cost-effective abatement, insights from the Company planning process, and alignment with our partners and other stakeholders. Capital investment guidance in lower-emission and other new investments is based on our corporate plan; however, actual investment levels will be subject to the availability of the opportunity set, stable public policy support, other factors, and focused on returns.
Energy demand modeling aims to replicate system dynamics of the global energy system, requiring simplifications. The reference to any scenario or any pathway for an energy transition, including any potential net-zero scenario, does not imply ExxonMobil views any particular scenario as likely to occur. In addition, energy demand scenarios require assumptions on a variety of parameters. As such, the outcome of any given scenario using an energy demand model comes with a high degree of uncertainty. For example, the IEA describes its NZE scenario as extremely challenging, requiring unprecedented innovation, unprecedented international cooperation, and sustained support and participation from consumers, with steeper reductions required each year since the scenario’s initial release. Third-party scenarios discussed in these reports reflect the modeling assumptions and outputs of their respective authors, not ExxonMobil, and their use or inclusion herein is not an endorsement by ExxonMobil of their underlying assumptions, likelihood, or probability. Investment decisions are made on the basis of ExxonMobil’s separate planning process but may be secondarily tested for robustness or resiliency against different assumptions, including against various scenarios. These reports contain information from third parties. ExxonMobil makes no representation or warranty as to the third-party information. Where necessary, ExxonMobil received permission to cite third-party sources, but the information and data remain under the control and direction of the third parties. ExxonMobil has also provided links in this report to third-party websites for ease of reference. ExxonMobil’s use of the third-party content is not an endorsement or adoption of such information.
ExxonMobil reported emissions, including reductions and avoidance performance data, are based on a combination of measured and estimated data. We assess our performance to support continuous improvement throughout the organization using our Environmental Performance Indicator (EPI) manual. The reporting guidelines and indicators in the Ipieca, the American Petroleum Institute (API), the International Association of Oil and Gas Producers Sustainability Reporting Guidance for the Oil and Gas Industry (4th edition, 2020, revised February 2023) and key chapters of the GHG Protocol inform the EPI and the selection of the data reported. Emissions reported are estimates only, and performance data depends on variations in processes and operations, the availability of sufficient data, the quality of those data and methodology used for measurement and estimation. Emissions data is subject to change as methods, data quality, and technology improvements occur, and changes to performance data may be updated. Emissions, reductions, abatements and enabled avoidance estimates for non-ExxonMobil operated facilities are included in the equity data and similarly may be updated as changes in the performance data are reported. ExxonMobil’s plans to reduce emissions are good-faith efforts based on current relevant data and methodology, which could be changed or refined. ExxonMobil works to continuously improve its approach to estimate, detect, measure, and address emissions. ExxonMobil actively engages with industry, including API and Ipieca, to improve emission factors and methodologies, including measurements and estimates.
Any reference to ExxonMobil’s support of, work with, or collaboration with a third-party organization within these publications do not constitute or imply an endorsement by ExxonMobil of any or all of the positions or activities of such organization. ExxonMobil participates, along with other companies, institutes, universities and other organizations, in various initiatives, campaigns, projects, groups, trade organizations, and other collaborations among industry and through organizations like the United Nations that express various ambitions, aspirations and goals related to climate change, emissions, sustainability, and the energy transition. ExxonMobil’s participation or membership in such collaborations is not a promise or guarantee that ExxonMobil’s individual ambitions, future performance or policies will align with the collective ambitions of the organizations or the individual ambitions of other participants, all of which are subject to a variety of uncertainties and other factors, many of which may be beyond ExxonMobil’s control, including government regulation, availability and cost-effectiveness of technologies, and market forces and other risks and uncertainties. Such third parties’ statements of collaborative or individual ambitions and goals frequently diverge from ExxonMobil’s own ambitions, plans, goals, and commitments. ExxonMobil will continue to make independent decisions regarding the operation of its business, including its climate-related and sustainability-related ambitions, plans, goals, commitments, and investments. ExxonMobil’s future ambitions, goals and commitments reflect ExxonMobil’s current plans, and ExxonMobil may unilaterally change them for various reasons, including adoption of new reporting standards or practices, market conditions; changes in its portfolio; and financial, operational, regulatory, reputational, legal and other factors.
References to “resources,” “resource base,” “recoverable resources” and similar terms refer to the total remaining estimated quantities of oil and natural gas that are expected to be ultimately recoverable. The resource base includes quantities of oil and natural gas classified as proved reserves, as well as quantities that are not yet classified as proved reserves, but that are expected to be ultimately recoverable. The term “resource base” is not intended to correspond to SEC definitions such as “probable” or “possible” reserves. For additional information, see the “Frequently Used Terms” on the Investors page of the Company’s website at www.exxonmobil.com under the header “Modeling Toolkit.” References to “oil” and “gas” include crude, natural gas liquids, bitumen, synthetic oil, and natural gas. The term “project” as used in these publications can refer to a variety of different activities and does not necessarily have the same meaning as in any government payment transparency reports.
Exxon Mobil Corporation has numerous affiliates, many with names that include ExxonMobil, Exxon, Mobil, Esso, and XTO. For convenience and simplicity, those terms and terms such as “Corporation,” “company,” “our,” “we,” and “its” are sometimes used as abbreviated references to one or more specific affiliates or affiliate groups. Abbreviated references describing global or regional operational organizations, and global or regional business lines are also sometimes used for convenience and simplicity. Nothing contained herein is intended to override the corporate separateness of affiliated companies. Exxon Mobil Corporation’s goals do not guarantee any action or future performance by its affiliates or Exxon Mobil Corporation’s responsibility for those affiliates’ actions and future performance, each affiliate of which manages its own affairs. For convenience and simplicity, words like venture, joint venture, partnership, co-venturer and partner are used to indicate business relationships involving common activities and interests, and those words may not indicate precise legal relationships. These publications cover Exxon Mobil Corporation’s owned and operated businesses and do not address the performance or operations of our suppliers, contractors or partners unless otherwise noted. In the case of certain joint ventures for which ExxonMobil is the operator, we often exercise influence but not control. Thus, the governance, processes, management and strategy of these joint ventures may differ from those in these reports. At the time of publication, ExxonMobil has completed the acquisitions of Denbury Inc. and Pioneer Natural Resources Company. These reports and the data therein do not speak of these companies’ pre-acquisition governance, risk management, strategy approaches, or emissions or sustainability performance unless specifically referenced.
These reports or any material therein are not to be used or reproduced without the permission of Exxon Mobil Corporation. All rights reserved.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR NON-GAAP AND OTHER MEASURES
The Positioned for Growth in a Lower-Emission Future section of the Advancing Climate Solutions Report mentions modeled operating cash flow in comparing different businesses over time in a future scenario. Historic operating cash flow is defined as net income, plus depreciation, depletion and amortization for consolidated and equity companies, plus noncash adjustments related to asset retirement obligations plus proceeds from asset sales. The Company’s long-term portfolio modeling estimates operating cash flow as revenue or margins less cash expenses, taxes and abandonment expenditures plus proceeds from asset sales before portfolio capital expenditures. The Company believes this measure can be helpful in assessing the resiliency of the business to generate cash from different potential future markets. The performance data presented in the Advancing Climate Solutions Report and Sustainability Report, including on emissions, is not financial data and is not GAAP data.


