News
2 min read
•Scale, storage and skills: Indonesia’s CCS difference
Key takeaways:
- Indonesia has the right geology to permanently store captured carbon emissions.
- Our scale and footprint across Asia Pacific allow us to collaborate across borders.
- CCS can be supported with existing infrastructure.
News
2 min read
•
In building a lower carbon future, it’s not just about the technology reducing the emissions, it’s also about the people. And when it comes to carbon capture and storage (CCS), the geology, the collaboration between countries and the right companies to invest are all a part of the equation.
Meet Cindy Kaharmen:
Cindy began her journey with ExxonMobil 17 years ago. During her career, Cindy gained extensive knowledge of reservoirs and geology before getting her MBA and moving to commercial and development planning roles.In her current role as a Low Carbon Solutions development planner, she now leads the effort to establish the best design and concept for upcoming CCS projects.
Asia Pacific is turning to CCS as one of the key solutions to help countries reduce CO2 emissions. One country that has an opportunity to become a strategic regional CCS hub is Indonesia.
Why CCS in Asia Pacific and Indonesia?
Let’s ask Cindy.
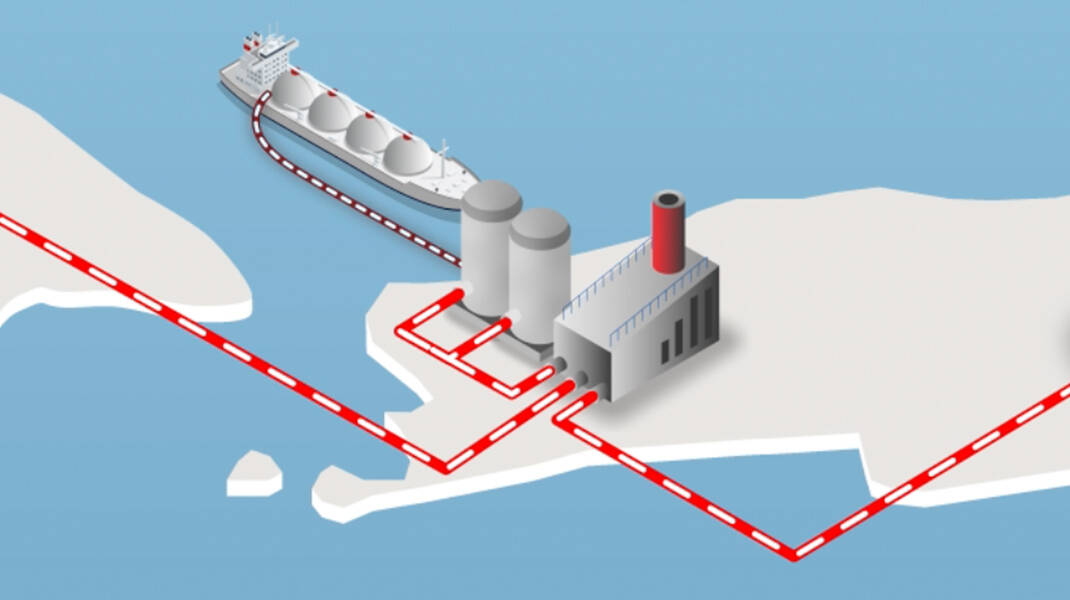
“What’s unique about CCS is that you need the right geology to safely and permanently store carbon from captured emissions. Not all countries have that. Indonesia not only has the right geology, but it also has decades of oil and gas experience and a lot of historical data.” CCS works by capturing CO2 emissions from industrial activity, especially from hard-to-abate sectors such as power plants, cement factories, and steel mills. The CO2 is removed at the source, compressed and transported for safe, secure, and permanent storage deep in underground geological formations.
Supporting existing infrastructure
The ability to work with existing infrastructure in Indonesia – rather than having to create entirely new systems – also plays a key role.“What’s great about CCS is that it lets existing infrastructure and industry keep going; you’re bolting this capture, transport and storage process to the back end of whatever ecosystem you have now, meaning you don’t need to start again from scratch,” Cindy says. “You just add it to what you have and keep moving forward.”

Low Carbon Solutions in Asia Pacific
Cindy believes that we are uniquely positioned to make it all happen with our knowledge of the geology and molecules and our scale and ability to connect the dots between countries.“Understanding what goes on below the ground is one thing but what makes ExxonMobil special in Asia Pacific is that we have had a significant presence in countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, Australia and Singapore. We’ve cultivated decades of wisdom in the region. We have grown experienced with local policies and regulations. All of that is not easy to replicate,”
“The other thing is scale and this is a real competitive advantage for ExxonMobil. Establishing and operating major cross-border businesses such as CCS takes global experience and great project management. We have an excellent track-record with both.”
We play a role in supporting lower-carbon solutions globally and this includes CCS. We plan to to invest more than $20 billion in initiatives to lower greenhouse gas emissions between 2022 and 2027.
Carbon capture and storage
Providing industry solutions needed to help reduce emissions during the energy transition
Explore more

Unlocking Asia Pacific’s CCS potential
4 min read
•
What could an Indonesian CCS hub look like?
2 min read
•

