selected item
Smart technologies for a smart refinery
From voice recognition to machine learning, ExxonMobil’s chemical and refining plants are installing a number of “smart technology upgrades” targeted at reducing emissions and increasing energy efficiency.
Driving energy efficiency with smart technologies
In particular, these technologies take aim at increasing energy efficiencies in manufacturing and have the potential to help ExxonMobil meet its 2025 emission reduction plans, a key step in aligning with the goals of the Paris Agreement.
Engineers and technology experts at ExxonMobil are applying the latest in assistance software, including artificial intelligence, to improve manufacturing efficiencies at the company’s chemical and refining plants. Similar to a driver turning on their GPS to navigate traffic or a homeowner using a smart thermostat to keep their home at the perfect temperature, plant operators at ExxonMobil’s Baton Rouge and Baytown refineries are piloting new, intelligent tools able to recommend more ideal operating conditions or isolate an improvement needed in their complex decision making. These advancements could decrease energy use and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Here are three advancements being developed or piloted around the world to revolutionize energy and chemicals production.
What’s that in the sky? Cognitive “Computer Vision” can tell us.
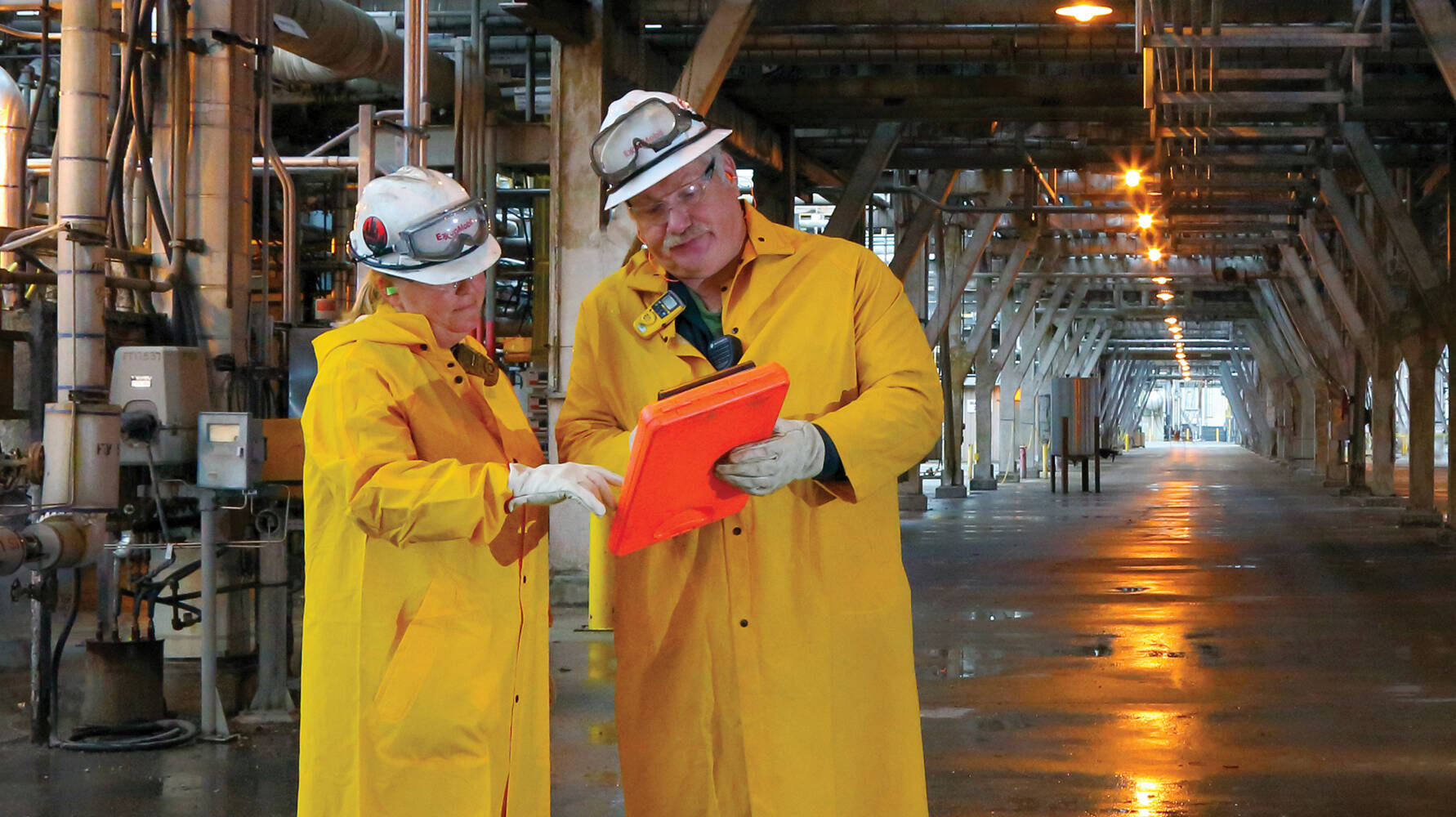
Meet Sofia, ExxonMobil’s Intelligent Operations Assistant.
Powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and voice recognition software, Sofia supports operators in the control room by helping them optimize daily production of high value fuels and chemicals. As such, by asking Sofia some pointed questions, operators can locate a piece of equipment not functioning at its best, such as a distillation unit not operating at its optimal temperature. It can also detect opportunities to speed up production. And most importantly, Sofia is self-learning, meaning that the more it assists operators, the better and more sophisticated it becomes at answering their questions.
Follow the “SmartLane” Artificial Intelligence guide.
Manufacturing essential feedstock for products like face masks, surgical gowns and hand sanitizer require quick adjustments to maintain the optimal temperature and the speed of chemical reactions in real time. That’s why ExxonMobil engineers developed “SmartLane.” Much like a GPS guides drivers to the most direct route, while avoiding traffic slowdowns, so too does SmartLane – except instead of calculating routes, it shows operators the optimal levels of a chemical ingredient needed to manufacture a specific product. The result is an energy-efficient plant where consistently optimal operations can save energy and time, which ultimately have the potential to reduce ExxonMobil’s GHG emissions footprint as compared to current operations.
Cutting down global emissions will take a portfolio of innovations, including scaled up carbon capture and storage, lower emission biofuels and energy-efficient technologies. Smart devices like Computer Vision, Sofia and Smart Lane are part of this complex effort and are providing operators with the critical tools they need to do much more with much less energy. In doing so, these tools are becoming one more part of the solution energy-efficient manufacturing.
Learn more about how ExxonMobil is working towards an energy-efficient, reduced-carbon future.
Explore more
10 surprising uses for oil and gas
While most people typically associate oil and gas products with transportation or heavy machinery, not all of it goes into fueling cars and jet planes or powering motors. From snow skis to shower curtains, oil and gas are versatile feedstocks that go into a host of everyday goods. Scroll down and learn about 10 of these items.2 min read

Energy efficiency
ExxonMobil constantly strives to improve performance and streamline our processes in order to improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Exploration technology
High-resolution seismic data combined with advanced computational analysis enable ExxonMobil to make the most informed exploration, development and production decisions.
Drilling and production technology
Our unique challenge consists of deploying technologies and methods to safely develop a wide range of resources both onshore and offshore in diverse locations around the world.
Hydraulic fracturing
Hydraulic fracturing enables companies like ExxonMobil to access unconventional oil and natural gas resources located in shale and tight-rock formations.