selected item
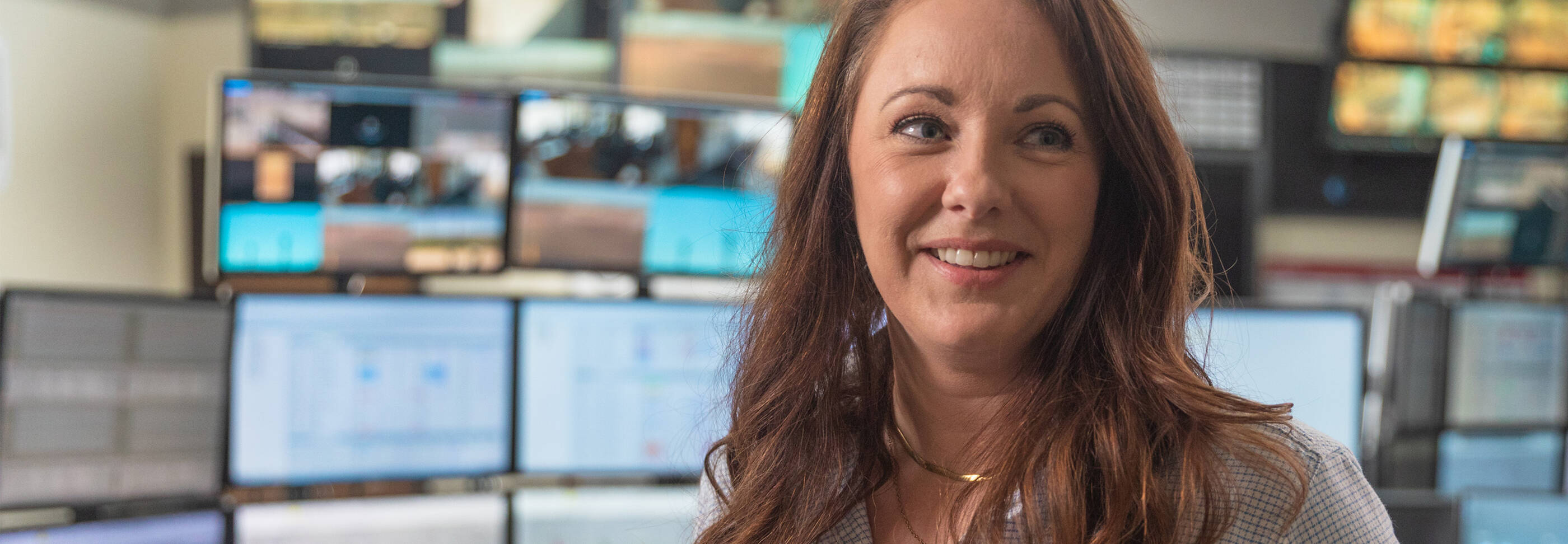
Anne Guinard, Safety and Environment Supervisor
Keeping people safe is Anne Guinard’s number-one priority. As the security, safety, health and environment supervisor at LaBarge, she’s focused on getting hundreds of employees home safely each day, and she plays a critical role in keeping the facility running smoothly.
Anne began her career as a safety adviser at ExxonMobil’s Canadian affiliate, Imperial Oil, before transferring to Houston. But it was LaBarge’s status as a center of carbon capture that drew her to Wyoming. She says she’s fascinated by the technology’s potential to reduce emissions, as well as LaBarge’s ability to serve as an example for future carbon capture sites around the globe. LaBarge’s future is also poised for growth, with an estimated $400 million expansion into carbon capture and storage planned to start up in 2025 – an ambitious undertaking that excites Anne.
Anne spoke with Energy Factor about her job and about how the facility’s operations can help chart a course for the rest of the world.
Explore more
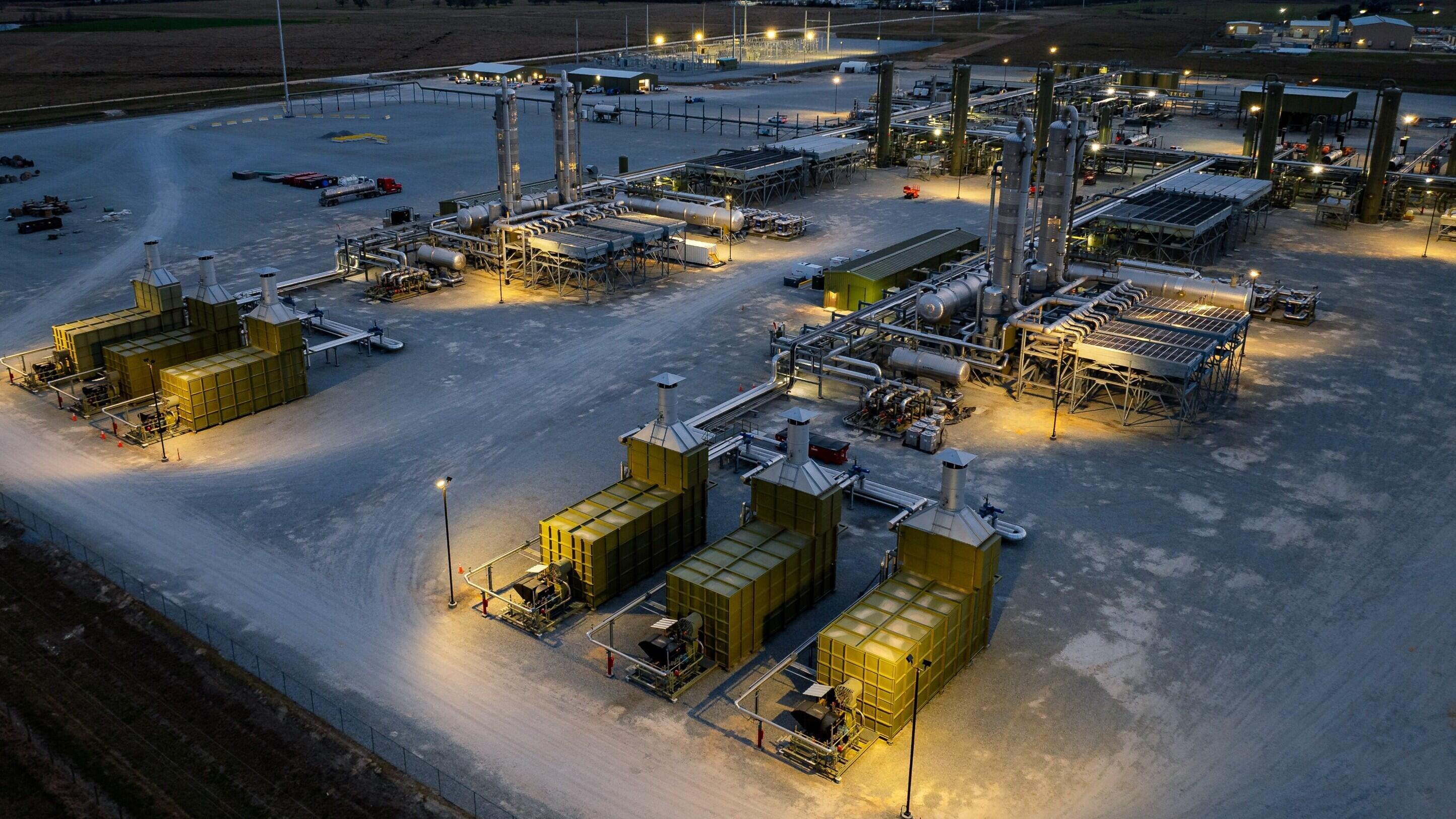

Expanding our CCS operations in Louisiana with another project startup
- We are now transporting and storing captured CO2 from the New Generation Gas Gathering (NG3) project in Gillis, Louisiana.
- NG3 is our second active commercial carbon capture and storage (CCS) operation in Louisiana.
- CCS application differentiates Louisiana’s core industries, including LNG, and provides a low-carbon energy solution for data centers and more.
2 min read
•
2025: Taking carbon capture and storage from momentum to impact
- We started up our first commercial CCS operation in 2025 with CF Industries in Louisiana.
- Our CCS portfolio spans multiple industries, with three projects expected to come online in 2026.
- We are targeting a final investment decision on our first Low Carbon Data Center by late this year.
2 min read
•
Capture it. Move it. Store it: Three steps for reducing CO2 emissions
- Want to learn more about carbon capture and storage (CCS)?
- Clay, Mark and Elizabeth are here to help in a video series.
- They explain how CCS works, why it matters and what makes it safe.
2 min read
•
How we’re capturing carbon and storing it safely
- In a new video, our Kathleen Ash explains how we’re keeping carbon capture and storage (CCS) safe.
- We have robust systems to safely transport and store captured CO2 emissions.
- We’re committed to protecting the safety of communities in which we operate.
2 min read
•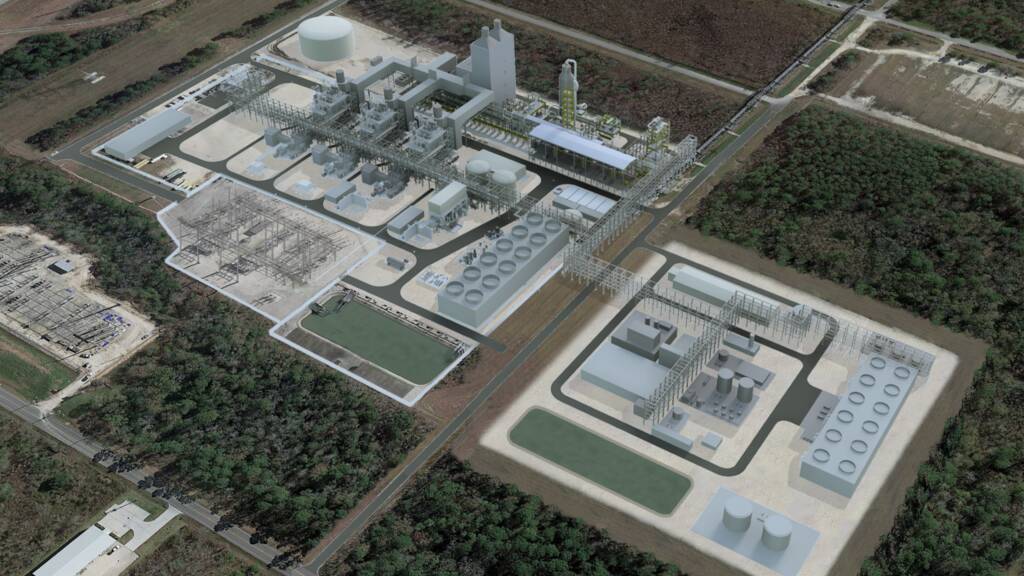
Calpine, ExxonMobil sign CO2 transportation and storage agreement for power generation project
- ExxonMobil to transport and store up to 2 million metric tons per year of CO2 from Calpine’s natural gas power generation facility.
- Calpine plans to produce ~500 megawatts of reliable low-carbon electricity, enough to power more than 500,000 homes.
- Project expected to bolster U.S. energy, strengthen industry competitiveness, and create jobs.
2 min read
•
2024: A breakout year for our carbon capture and storage business
- We’re leading the creation of a new industry.
- 2024 was a big year for our CCS business.
- More milestones are ahead in 2025.
3 min read
•